By Dr Shariq Nisar
Corporate Governance refers to the set of systems, principles and processes basis, which a company is governed. Aim of Corporate Governance is to promote corporate fairness, transparency and accountability. Over the years, Corporate Governance has become the cornerstone of good business practices. It encompasses the processes, practices and policies that a company relies on to make formal decisions and to manage the organisation. The concept of Corporate Governance is becoming increasingly important for companies in India, as the companies are becoming increasingly aware of their public image and realising the importance to behave ethically. There is increasing empirical evidence that good governance correlates with increased shareholder value and particularly bad governance is a red flag for increased risk.
The primary focus of Corporate Governance starts with the board of directors, how the board conducts itself and how it governs the company as it is mainly the responsibility of the board of directors to ensure good Corporate Governance.
Elements of Corporate Governance:
Principle 1: The corporate governance framework must help promote transparent and fair markets and the efficient allocation of resources.
Principle 2: The corporate governance framework must identify basic shareholder rights and provide equitable treatment of all shareholders.
Principle 3: The corporate governance framework must disclose and minimize conflicts of interest of market participants.
Principle 4: The corporate governance framework must encourage active co-operation between companies and their stakeholders.
Principle 5: The corporate governance framework must facilitate the disclosure of material information to aid in informed decision-making.
Principle 6: The corporate governance framework must ensure effective supervision by the board and enhance the board accountability to stakeholders.
Corporate Governance Parameters
- Board Effectiveness: This relates to the Board’s objective oversight of the company’s actions. Whether the company has a strong board composition with diversity across skills and a non-executive chairperson or not.
- Conflict of Interest:Disclosure and minimization of conflicts of interests and strong internal controls systems to address conflicts in related party transactions (RTP).
- Stakeholder Management:Active co-operation between corporations and stakeholders to pursue the corporate governance agenda. Well-articulated supplier or vendor selection and management policies.
- Executive Remuneration:Judicious remuneration closely aligned with company growth.
Benefits of Corporate Governance:
- Ensures corporate success and economic growth.
- Maintains investors’ confidence, which helps in lowering the capital cost and bringing a positive impact on the share price.
- Minimizes wastages, corruption, risks and mismanagement.
- Helps in brand formation and development.
Indian Corporate Governance Scorecard:
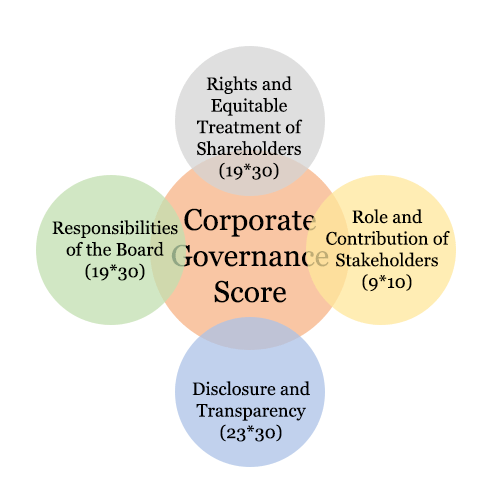
The Corporate Governance Scorecard is an initiative of the BSE and International Finance Corporation (IFC). Institutional Investor Advisory Services (IiAS) is the technical partner responsible for preparing the scorecard. The Scorecard is an assessment of the Corporate Governance practices of a company. The Scorecard builds upon the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) principles of Corporate Governance and draws on the lessons from global best practices. Besides, the Scorecard also considers the Indian context. Overall, the idea behind the Scorecard is to recognise the current level of corporate governance practices and help companies enhance these to globally relevant levels. Following are the four parameters on which the Indian Scorecard is based:
- The Rights and Equitable Treatment of Shareholders
- Role and Contribution of Stakeholders
- Disclosure and Transparency
- The Responsibilities of the Board (Effective supervision and accountability)
Benefits of Scorecards:
- Increased awareness and greater visibility of global best practices;
- Greater investor insight into corporate governance;
- An opportunity to review and analyze the quality of corporate governance within companies and economies;
- Assists regulatory institutions to identify strengths and weaknesses in corporate governance practices; and
- Motivation to enhance company’s corporate governance practices beyond the minimal requirements of laws and regulations;
Evaluation Framework:
The scorecard comprising 70 questions is categorised under the four principles. The scoring is based on three marking techniques:
- 0, 1 or 2 points (0 being the lowest and 2 being the highest)
- The information disclosed must be available in public to corroborate
- Whether the company needs to improve on the given element of Corporate Governance, as asked by the question or follows at least Indian standard, or follows a global practice
- 0 or 2 points for yes/no questions. Negative responses attract 0 points, positive responses attract 2 points
- Questions marked as ‘Not applicable’ are not given any mark and the question is excluded from the final marking
- The non-applicability of a particular question leads to exclusion of the question for overall score calculation. This may bring down the score for the company which may not reflect the correct picture.
Further, each of the four principles on which the questions are based, have been assigned weights based on:
- Number of questions under each of the category
- The relative importance of the questions in that category
| Category | Number of Questions | Category Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Rights and equitable treatment of shareholders | 19 | 30 |
| Rights and equitable treatment of shareholders | 9 | 10 |
| Rights and equitable treatment of shareholders | 23 | 30 |
| Rights and equitable treatment of shareholders | 19 | 30 |
| Total | 70 | 80 |
Based on the scores calculated by the above method, companies are then categorised into four: The category reflects their adoption of corporate governance practices.
| Score | Category based on the adoption of Corporate Governance practices |
|---|---|
| >= 70 | Leadership |
| 60-69 | Good |
| 50-59 | Fair |
| <50 | Basic |
Observartions:
The first Indian Corporate Governance Scorecard was released in December 2016 when 30 companies were assessed. In 2017, scorecards of 100 companies published. In 2019, in addition to the companies in BSE100, 50 recently listed companies were also added to the Scorecard.
BSE has also developed a CGS Tool Kit, which makes it convenient for all listed companies to conduct a self-evaluation using the scorecard criteria and methodology. Companies would do well to check their scores.






0 Comments